The evaluation of pupillary reaction is a critical aspect of any neurological examination. Pupillary response provides valuable information about the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, and changes in pupillary size can indicate various neurological conditions. Two opposing muscles control pupil size, the constrictor and the dilator muscles innervated by the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, respectively. In this article, we will discuss the concept of pupillary response, its importance, and the significance of percent change in pupil size.
What is Pupillary Response?
Pupillary response refers to the changes in the pupil’s size in response to different stimuli. The size of the pupil can change in response to light, emotions, drugs, or any other factor that influences the autonomic nervous system. The constrictor and dilator muscles control the size of the pupil, and the balance between their activities determines the size of the pupil.
When the constrictor muscle contracts, the pupil size decreases, and the pupil size increases when the dilator muscle contracts. The pupillary response is a complex interaction between the central nervous system, the autonomic nervous system, and the sensory inputs from the eyes. Doctors can use pupil size to evaluate the autonomic nervous system’s functioning and diagnose various neurological conditions.
Why Evaluate Pupillary Response
The evaluation of the pupillary response in traumatic brain injury is an important part of a neuro exam. It provides valuable information about a patient’s neurological state. The pupillary response is used to diagnose various neurological conditions, including traumatic brain injury (TBI). In TBI, changes in pupillary size can indicate an intracranial hematoma, a dangerous condition that requires immediate treatment.
Pupillary response and various neurological tools are also used to evaluate the functioning of the autonomic nervous system. In some neurological conditions, such as Horner’s syndrome, the pupil size can be affected, which can provide valuable information about the location and extent of the injury. In addition, doctors can use the pupillary response to assess the effects of drugs on the autonomic nervous system.
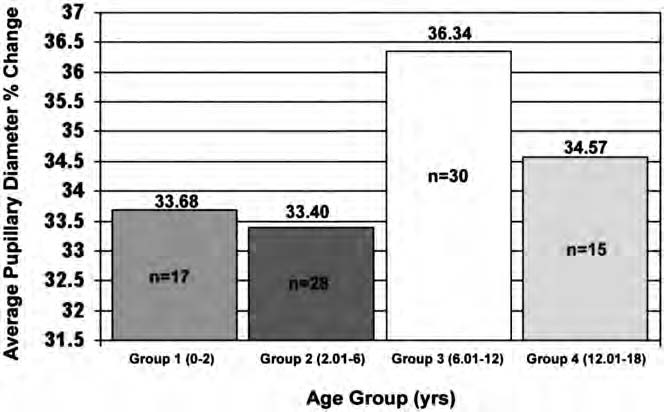
Understanding Percent Change in Pupil Size
Percent change in pupil size refers to the change in pupil size as a percentage of the original size. It is calculated by dividing the change in pupil size by the original size and multiplying by 100. This provides a standard way of evaluating the pupillary response, as the percentage change is independent of the original size of the pupil.
Percent change in pupil size has significant diagnostic value, especially in evaluating pupillary response in TBI. A large pupil size change can indicate a potentially dangerous condition, such as an intracranial hematoma. Experts can also use the percent change in pupil size to evaluate the effects of drugs on the autonomic nervous system.
However, it is important to note that a percent change in pupil size is not a perfect diagnostic tool and has several limitations. For example, the accuracy of the measurement can be affected by various factors, such as the lighting conditions and the method used for measuring pupil size. In addition, the percent change in pupil size does not provide information about the direction of the change in pupil size, i.e., whether the pupil is constricting or dilating. Therefore, it is important to consider other aspects of the pupillary response, such as the speed and pattern of the change, to accurately interpret the results.
Using Pupillary Response as a Neurological Tool
The pupillary response is an important tool for evaluating the neurological state of a patient. It provides valuable information about the functioning of the autonomic nervous system. It can diagnose various neurological conditions, such as TBI. The evaluation of pupillary response is an important part of the neuro exam. It should be performed as a standard procedure in any neurological evaluation.
There are several methods for evaluating the pupillary response, including observation of the pupil size, measurement of the pupil size, and assessment of the pupillary light reflex. The choice of method depends on the specific clinical scenario and the required information.
NPi as a Measure of Pupillary Response
The neurological pupil index (NPi) is a new pupillary response measure developed to improve the accuracy and reliability of pupillary response evaluation. NPi is based on a mathematical model of the pupillary response and provides a more accurate and consistent measure of the pupillary response than traditional methods.